Signalment:
3-year-old, gelding, quarter horse, (
Equus caballus) equineThe patient presented with muscle fasciculations, hyperhidrosis, tachycardia (88 bpm) and tachypnea.
The temperature was within normal limits and capillary refill time was prolonged. ECG revealed sinus
tachycardia. Laboratory abnormalities included mild thrombocytopenia, azotemia (creatine 4.8), hyperglycemia
(glucose 483), hypokalemia (K 3.0), hyponatremia (Na 120), hypochloremia (Cl 81), hyperbilirubinemia (4.6)
and elevated CK (5050) and AST (927).
Gross Description:
An adult quarter horse gelding (500 kg) in good flesh with mild postmortem autolysis
is presented for necropsy. The cranioventral lungs, representing approximately 20% of the lung parenchyma,
are sharply demarcated, dark green, and consolidated with marked expansion of the interlobular spaces by edema and
yellow friable material (fibrin). The trachea and bronchial airways are filled with white foam; clear fluid oozes from
the cut section. The remaining lung tissue is rubbery and partially collapsed. The cranioventral pulmonary
pleura is covered by a thin layer of brown friable material (fibrin). The pericardial sac contains ~ 200 mls of dark
yellow fluid. There is pale tan streaking throughout the myocardium of the ventricular free wall and the
interventricular septum; the left ventricular free wall appears most severely affected. This discoloration affects
greater than 40% of the myocardium. The liver is mildly firm and has an accentuated lobular pattern. There are
several dozen subcapsular hemorrhages in both kidneys. Approximately 40% of the glandular stomach is thickened
and hyperemic; about half of this area is covered by a fibrinous pseudomembrane. The stomach contains grain
and hay/grass ingesta. The small colon contains formed feces. Urine is clear and yellow. There is mild edema of
the lamina of P3 in the right front and left rear feet.
Histopathologic Description:
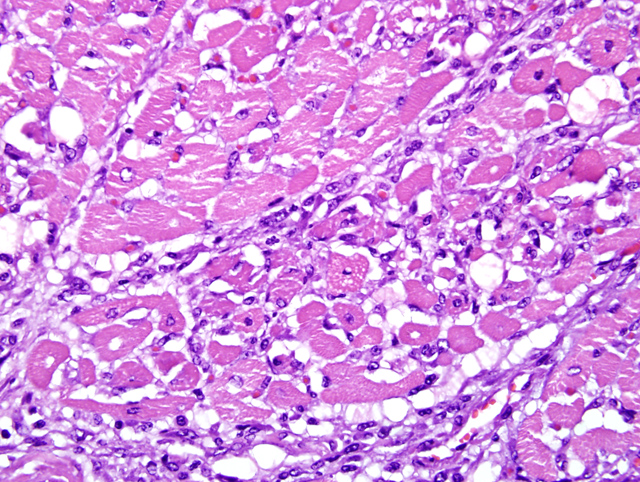
Heart: Multifocal myocardial degeneration and necrosis are present within
multiple sections of heart, affecting approximately
25% of the myocardium. The change is characterized
by loss of myocardial cross striations, fragmentation,
and vacuolation of myocardial cytoplasm, and nuclear
pyknosis and karyolysis (
Fig. 1-1). Sarcolemmal sheaths
are collapsed, satellite cell nuclei are plump and closely
arranged, and there are moderate numbers of macrophages
with fewer lymphocytes and occasional neutrophils in the
affected areas. Perivascular supporting tissues and tissues
surrounding Purkinje cells are expanded by edema fluid or
finely granular, basophilic, loose mucinous material.
Morphologic Diagnosis:
Heart:
Myocardial degeneration and necrosis, severe, multifocal
to coalescing, subacute, quarter horse,
Equus caballus
Lab Results:
Mild thrombocytopenia
Azotemia (creatinine 4.8)
Hyperglycemia (glucose 483)
Hypokalemia (K 3.0)
Hyponatremia (Na 120)
Hypochloremia (Cl 81)
Hyperbilirubinemia (4.6)
Elevated CK (5070)
Elevated AST (927)
Condition:
Clenbuterol toxicosis
Contributor Comment:
This horse is one of several that died or were euthanized after being given clenbuterol.
In addition to the myocardial necrosis, the horse had varying degrees of skeletal muscle necrosis in different
muscle groups. High levels of clenbuterol were found in this horses serum the day after dosing, and clenbuterol
overdose is believed to be responsible for the clinical signs of muscle fasciculation, tachycardia, and hyperhydrosis
seen at presentation, as well as for the skeletal and cardiac muscle degeneration and necrosis seen grossly and
histologically.
Clenbuterol is a beta-2 sympathomimetic, with most of the
pharmacologic activity coming from the levo form.
4 The
drug is used as a bronchodilator in horses and non-lactating
cattle at a recommended dosage of 0.8 micrograms per
kilogram of body weight.
4 Excretion is primarily via urine
as unmetabolized clenbuterol. Four studies have shown
that clenbuterol induces myocardial necrosis in laboratory
rats
1, 2, although a recent study of the relative myotoxicity
of clenbuterol versus other beta agonists showed that
clenbuterol is less myotoxic than fenoterol, another beta-2
sympathomimetic.
3
In this case, further history revealed a questionable
source of clenbuterol that, when tested at the LSU
Analytical Systems Laboratory, contained 67.4 times the
FDA approved level of the drug. The bottle was labeled
Clenbuterol HCl, 72.5 mcg/ml, 0.5 ml/100lb, but actually
contained 5.0 mg/ml instead of the labeled 72.5 mcg/ml,
or 0.0725 mg/ml. The horse was given clenbuterol from
this bottle five days prior to euthanasia.
JPC Diagnosis:
Heart, left ventricle: Myocardial
degeneration and necrosis, multifocally extensive,
moderate, with histiocytic and lymphocytic myocarditis
and fibroplasia
Conference Comment:
Catecholamines and
catecholamine receptor agonists are believed to cause
myocardial necrosis in various settings including
brain-heart syndrome, pheochromocytoma and
sympathomimetic drug overdoses. Numerous toxins
cause myocardial necrosis as well.
Ionophore toxicity occurs in horses and other monogastrics
that are mistakenly fed coccidiostats used in ruminant and
poultry feed.
4
Cardiac glycosides are found in several different plants
in various parts of the world, and ingestion often causes
death within a few hours with little to no gross or histologic
footprint.
4These glycosides inhibit the sodium-potassium
ATPase pump causing a disruption in ion concentration
and membrane potential leading to muscle necrosis.
4
Diagnosis is often based on discovery of the offending
plant in the gastrointestinal system or circumstantial
evidence.
4
Some toxic alcohols, such as gossypol and tremetol, can
cause myocardial necrosis. Gossypol, often found in
cottonseed meal used as a protein supplement in feed,
causes myocardial necrosis in young ruminants, pigs,
and dogs.
4 Tremetol is the toxic principal in
Eupatorium
rugosum (white snakeroot).
4
Horses ingest blister beetles in dried hay, and the canthardin
present in the insects causes gastric lesions, hemorrhagic
cystitis, enterocolitis, and myocardial necrosis.
4 Hairy
vetch (
Vicia villosa) can also cause myocardial lesions
in cattle but not horses. Histologic lesions consist of
monocytes, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and giant cells. In
cattle, eosinophils are also present.
5
References:
1. Burniston JG, Chester N, Clark WA, Tan LB,
Goldspink DF: Dose-dependent apoptotic and necrotic
myocyte death induced by the beta2-adrenergic receptor
agonist, clenbuterol. Muscle Nerve
32:767-774, 2005
2. Burniston JG, Ng Y, Clark WA, Colyer J, Tan LB,
Goldspink DF: Myotoxic effects of clenbuterol in the rat
heart and soleus muscle. J Appl Physiol
93:1824-1832,
2002
3. Burniston JG, Tan LB, Goldspink DF: Relative
myotoxic and haemodynamic effects of the betaagonists
fenoterol and clenbuterol measured in conscious
unrestrained rats. Exp Physiol
91:1041-1049, 2006
4. EMEA: Clenbuterol Hyodrochloride Summary
Report (1), ed. Products CfVM. European Agency for the
Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines
and Information Technology Unit, 2000
5. Ginn, PE, Mansell JEKL, Rakich PM: Skin and
appendages.Â
In: Jubb, Kennedy, and Palmers Pathology
of Domestic Animals, vol. 1 ed. Maxie MG, pp. 619-620.
Elsevier Limited, Philadelphia, PA, 2007
6. Maxie MG, Robinson WF: Cardiovascular system.
In: Jubb, Kennedy and Palmers Pathology of Domestic
Animals, vol. 3 ed. Maxie MG, 5th ed., pp. 32-33. Elsevier,
Philadelphia, PA, 20073. Burniston JG, Tan LB, Goldspink DF: Relative
myotoxic and haemodynamic effects of the betaagonists
fenoterol and clenbuterol measured in conscious
unrestrained rats. Exp Physiol 91:1041-1049, 2006