Signalment:
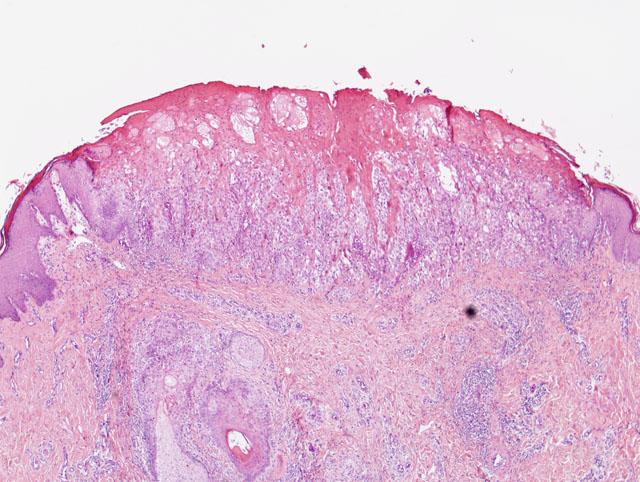
Gross Description:
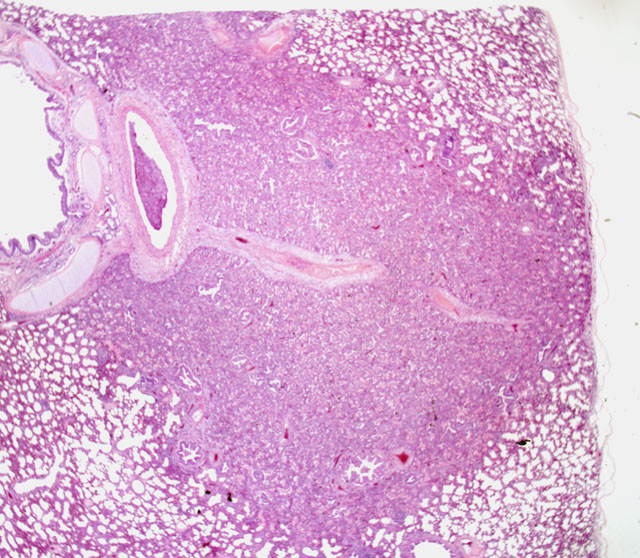
Histopathologic Description:
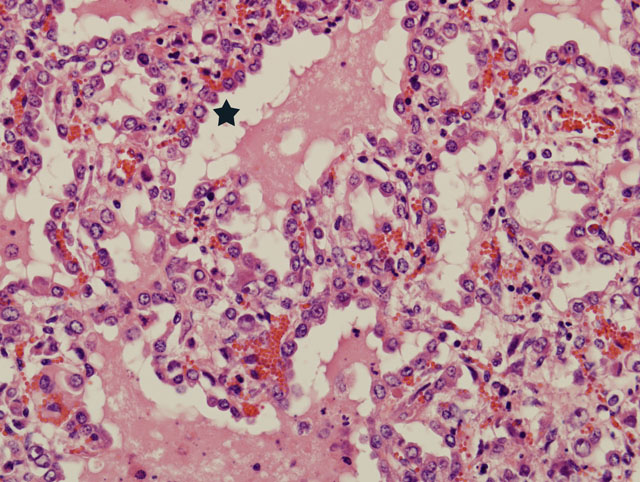
The bronchi, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles showed varying degrees of epithelial hyperplasia, necrosis, and ballooning degeneration, with squamous metaplasia. In severely affected areas, alveolar septa were thickened as a result of pneumocyte hypertrophy. Alveolar spaces were commonly filled with fibrin, proteinaceous exudates, necrotic cellular debris, macrophages, edematous fluid with foci of alveolar septal necrosis, and septal vascular thrombi with vasculitis (Fig. 3-3). Peribronchiolar and perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates were evident in some areas. Similar inclusion bodies were also detected in histiocytes, fibroblasts, epithelial cells and pneumocytes. There was lymphoid depletion along with histiocytosis in the spleen and lymph nodes, with necrosis and numerous inclusion bodies in histiocytic cells.
Morphologic Diagnosis:
2. Lung: Bronchointerstitial pneumonia, hyperplasia, severe, multifocal, chronic, with ballooning degeneration, vasculitis, and eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies.
Lab Results:
Condition:
Contributor Comment:
Clinically, infected animals can have acute to chronic disease characterized by generalized pox lesions throughout the skin and mucous membranes accompanied with persistent fever, lymphadenitis, and often a focal viral pneumonia.Â
The differential diagnosis should include contagious pustular dermatitis (Orf), peste des petits ruminants, and bluetongue. Orf is an endemic disease in Taiwanese goat herds.
PCR for detecting Capripox or Orf virus by the primer pair CPVS, CPVA (413 bp) and OVS, OVA (708 bp) (Zheng M. et al) respectively was employed for final diagnosis of this case. The source of the outbreak, however, is inconclusive.
JPC Diagnosis:
Lung: Pneumonia, bronchointerstitial, proliferative, subacute, multifocal, moderate, with intraepithelial intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusion bodies.
Conference Comment:
| GENUS | VIRUS | MAJOR HOSTS |
| Orthopoxivirus | Variola virus (smallpox) Vaccinia virus Cowpox virus Camelpox virus Ectromelia virus Monkeypox virus Seal poxvirus |
Humans Humans, cattle, swine, rabbits Humans, cattle, cats, rats Camels Mice Humans, non-human primates Grey seals |
| Capripoxivirus | Sheeppox virus Goatpox virus Lumpyskin disease virus |
Sheep, goats Goats, sheep Cattle, cape buffalo |
| Suipoxvirus | Swinepox virus | Swine |
| Leporipoxvirus | Molluscum contagiosum virus | Humans, horses |
| Yatapoxvirus | Yabapox virus and tanapox virus |
Humans, non-human primates |
| Avipoxvirus | Fowlpox virus | Chickens, turkeys |
| Parapoxvirus | Orf virus Pseudocowpox virus Bovine papular stomatitis virus |
Sheep, goats, humans Cattle, humans Cattle, humans |
Poxviruses are epitheliotropic viruses, and in some instances, such as with smallpox, sheeppox, goatpox monkeypox, or ectromelia, they can cause generalized, severe, or fatal disease. Grossly, poxvirus lesions progress from an initial macule, to a papule, to a vesicle, ending in pustule and and crust formation. Histologically, poxvirus infection often causes proliferation of cells within the stratum spinosum with ballooning degeneration and eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions.(2,4)
References:
2. Ginn PE, Nasell JEKL, Rakich PM: Skin and appendages. In: Jubb, Kennedy and Palmers Pathology of Domestic Animals, ed. Maxie MG, 5th ed., pp. 297-298. Elsevier Limited, Edinburgh, UK, 2007
3. Kitching RP, Hammond JM, Black DN: Studies on the major common precipitating antigen of capripoxvirus. J Gen Virol 67:139-148, 1986
4. Murphy FA, Gibbs EPJ, Horzinek MC, Studdert MJ: Poxviridae. In: Veterinary Virology, 3rd ed., pp. 277-291. Academic Press, San Diego, California, 1999
5. Parthiban M, Govindarajan R, Manoharan S, Purushothaman V, Chandran NDJ, Koteeswaran A: Comparative sequence analysis of diagnostic PCR amplicons from Indian sheeppox virus. Vet Arhiv 75:203-209, 2005
6. Zheng M, Liu Q, Jin N, Guo J, Huang X, Li H, Zhu W, Xiong Y: A duplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection and differentiation of Capripoxvirus and Orf virus. Mol Cell Probes 21:276-81, 2007